[Coding045] LeetCode 316
Remove Duplicate Letters
Get the knowledge flowing and circulating! :)
目录
※ 本题收获
第一版整个代码的撰写过程耗时2小时,最终得到了一个通过了277/290个样例的结果。
缺点总结
按部就班的思维,有点呆板。
我的思考是按照程序的逻辑对每个可能的情况进行判断,然后逐渐改善代码。
参数命名不够合适。
代码1的参数命名和代码2的参数命名对比如下:
xxxxxxxxxx41// 代码12int[] visited = new int[1000]; // 本该计数的,我用了visited(常用于boolean)3boolean[] ok = new boolean[1000]; // ok这个命名也太low了4char[] chs = s.toCharArray();xxxxxxxxxx41// 代码2(推荐参考)2int[] countArray = new int[26]; // 只要26个,下标用[ch - 'a']即可;3boolean[] visited = new boolean[26]; // 默认情况下都没有被访问(默认值:false)4for(char c : s.toCharArray())
特判没有思考清楚。
耗时太久,如果超过1个小时没搞定,要记得及时观看答案!不要耗时太久,因为一天还有其他重要的事要做呢!
题目:316. Remove Duplicate Letters
Given a string s, remove duplicate letters so that every letter appears once and only once. You must make sure your result is the smallest in lexicographical order among all possible results.
Example 1:
xxxxxxxxxx21Input: s = "bcabc"2Output: "abc"
Example 2:
xxxxxxxxxx21Input: s = "cbacdcbc"2Output: "acdb"
Constraints:
1 <= s.length <= 104sconsists of lowercase English letters.
Note: This question is the same as 1081: https://leetcode.com/problems/smallest-subsequence-of-distinct-characters/
代码1(配 · 手绘过程图)
xxxxxxxxxx1401//错误代码2class Solution {3 public String removeDuplicateLetters(String s) {4 int[] visited = new int[1000];5 boolean[] ok = new boolean[1000];6
7 char[] chs = s.toCharArray();8 for (char each : chs)9 {10 visited[each]++;11 }12
13 Stack<Character> stack = new Stack();14
15 System.out.println('a' - 'c');16
17 stack.push(chs[0]);18 visited[chs[0]]--;19 ok[chs[0]] = true;20 for(int i = 1; i < chs.length; i++)21 {22 if(chs[i] <= stack.peek())23 {24 while (!stack.empty() && visited[stack.peek()] > 0 && chs[i] <= stack.peek())25 {26 ok[stack.pop()] = false;27 } 28 }29
30 if (ok[chs[i]] == false)31 {32 stack.push(chs[i]);33 visited[chs[i]]--;34 ok[chs[i]] = true;35 }36
37 }38 StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();39 for(char e : stack)40 {41 res.append(e);42 }43 return res.toString();44 }45}46
47// Wrong Answer: 277 / 290 testcases passed48// "abacb" → "abc" not "acb"49
50
51// 改正版:52class Solution {53 public String removeDuplicateLetters(String s) {54 int[] visited = new int[1000];55 boolean[] ok = new boolean[1000];56
57 char[] chs = s.toCharArray();58 for (char each : chs)59 {60 visited[each]++;61 }62
63 Stack<Character> stack = new Stack();64
65 stack.push(chs[0]);66 visited[chs[0]]--;67 ok[chs[0]] = true;68 for(int i = 1; i < chs.length; i++)69 { 70 visited[chs[i]]--;71
72 if (ok[chs[i]] == true)73 continue;74
75 if(chs[i] <= stack.peek())76 {77 while (!stack.empty() && visited[stack.peek()] > 0 && chs[i] <= stack.peek())78 {79 ok[stack.pop()] = false;80 } 81 }82
83 if (ok[chs[i]] == false)84 {85 stack.push(chs[i]);86 ok[chs[i]] = true;87 }88
89 }90 StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();91 for(char e : stack)92 {93 res.append(e);94 }95 return res.toString();96 }97}98
99
100// 改正版(精简后):101class Solution {102 public String removeDuplicateLetters(String s) {103 int[] visited = new int[1000];104 boolean[] ok = new boolean[1000];105
106 char[] chs = s.toCharArray();107 for (char each : chs)108 {109 visited[each]++;110 }111
112 Stack<Character> stack = new Stack();113
114 stack.push(chs[0]);115 visited[chs[0]]--;116 ok[chs[0]] = true;117 for(int i = 1; i < chs.length; i++)118 { 119 visited[chs[i]]--;120
121 if (ok[chs[i]] == true)122 continue;123
124 while (!stack.empty() && visited[stack.peek()] > 0 && chs[i] <= stack.peek())125 {126 ok[stack.pop()] = false;127 } 128
129 stack.push(chs[i]);130 ok[chs[i]] = true;131
132 }133 StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();134 for(char e : stack)135 {136 res.append(e);137 }138 return res.toString();139 }140}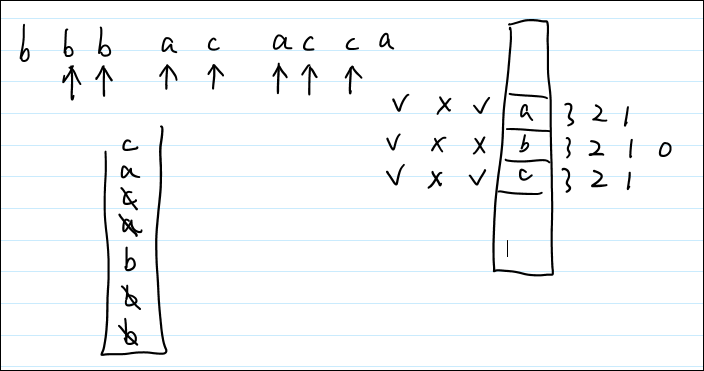
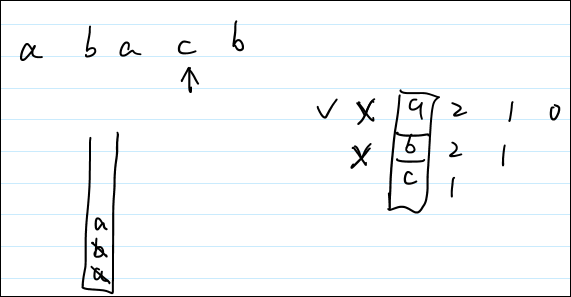
代码解读 | 评价
这个特殊情况的解读在代码2的
line26~line35。
####
代码2
xxxxxxxxxx531class Solution {2 public String removeDuplicateLetters(String s) {3 int[] countArray = new int[26]; // 只要26个,下标用[ch - 'a']即可;4
5 // aaccb6 // a:27 // b:18 // c:29 for (char c : s.toCharArray()) // 计算每个字母出现的次数10 {11 countArray[c - 'a']++;12 }13
14 // 确定字母是否被访问了(是/否)15 boolean[] visited = new boolean[26]; // 默认情况下都没有被访问(默认值:false)16
17 Stack<Character> st = new Stack();18
19 for(char c : s.toCharArray())20 {21 countArray[c - 'a']--; // 不管怎样,每次访问后,数量肯定减122
23 if (visited[c - 'a']) 24 continue; // 如果c被访问了,就继续循环25 26 // continue这句话的含义是:27 // 如果想要pop()栈里面的元素,请你找还没出现的元素来跟我比;28 // 别用已经出现的元素来跟我比,那我肯定比不过~。29 // 示例:a b a c b30 // 对于这个案例中,如果按照出错的代码1,表示的是,遇到第2个a【a b (a) c b】的时候,把栈内的a,b都pop(),这是不合理的,因为a已经是王者级别的存在了,你用a可以扫清栈里的所有元素,这样肯定出错。31 // 相反,如果你用c或者b来和当前的栈顶比较时,是比较合理的:因为c如果比b小,那么c把它踢出去合情合理;如果c没有b小,那么b就安安稳稳的待着,别人别想动他!32
33 // 条件1:栈如果想要执行pop()操作,必须不为空,否则报错34 // 条件2:题干要求的是当前字符在已入栈的栈顶字符之前(所以要小于栈顶元素)35 // 条件3:栈顶元素pop()的前提是后续的字符串里还有同样的字符36 while (!st.empty() && c < st.peek() && countArray[st.peek() - 'a'] > 0)37 {38 visited[st.peek() - 'a'] = false; // 栈顶元素设置为没有访问39 st.pop(); // 栈顶元素出栈40 }41
42 st.push(c); // 当前元素入栈43 visited[c - 'a'] = true; // 标记当前元素为已访问44 45 }46 StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();47 for(char e : st)48 {49 res.append(e);50 }51 return res.toString();52 }53}代码解读 | 评价
第一版代码错误的原因就是“a b a c b”这个测试用例没有分析仔细。具体的分析过程如代码line24所示。
特别注意,continue的含义!